The South Manchuria Railway (SMR) was founded in 1906 in Dalian. The first president was Goto Shimpei.
By the end of 1907, the company employed nearly 13.000 people. By 1910, those numbers had increased to 35,000 and 25,000 respectively.The railway used a significant amount of US-made rails and signaling equipment, as well as some steam locomotives built by the American Locomotive Company at Dunkirk, NY. A visiting executive from the Erie Railroad was quite impressed with the arrangement, and described South Manchurian Railway ca. 1913 as "the only railroad in the whole world that is like our American railroads (and they are, fairly speaking, the best)".
The SMR quickly expanded the system inherited from Russia to staggering proportions, building coal mines at Fushun and Yantai, and harbor facilities at Andong, Yingkou, and Dalian. At each station, the SMR built hotels for travelers and warehouses for goods.
From 1916, the SMR began to spin off a number of subsidiary companies, including Showa Steel Works, Dalian Ceramics, Dalian Oil & Fat, South Manchurian Glass, as well as flour mills, sugar mills, electrical power plants, shale oil plants and chemical plants.
Over 75% of SMR's income was generated by its freight business, with the key to profitability coming from soybean exports, to other asian countries and to Europe. Soybean production increased exponentially with increasing demand for soy oil, and for soy meal for use in fertilizer and animal feed. By 1927, half of the world's supply of soybean was from Manchuria.
By 1938, the SMR had 72 subsidiary companies, development projects in 25 urban areas and carried 27,515,000 passengers per year.
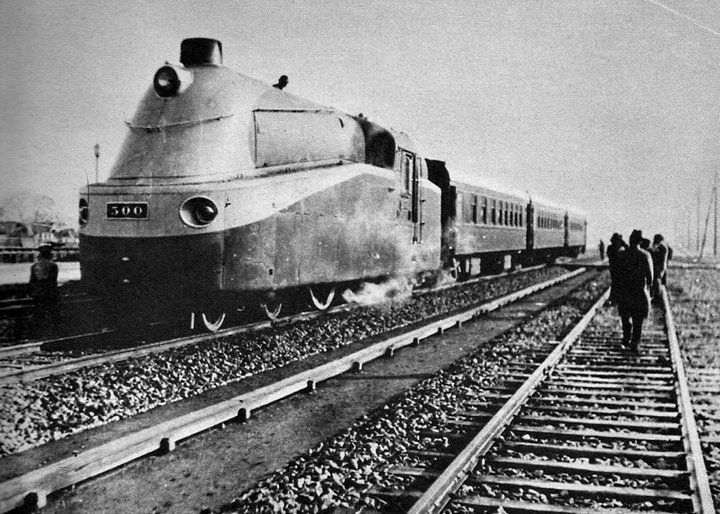
The "Asia Express " is the famous train of the SMR.
The SMR is at present one of the biggest company in the Empire of China, it's actual president of the SMR is Duan Junyi.
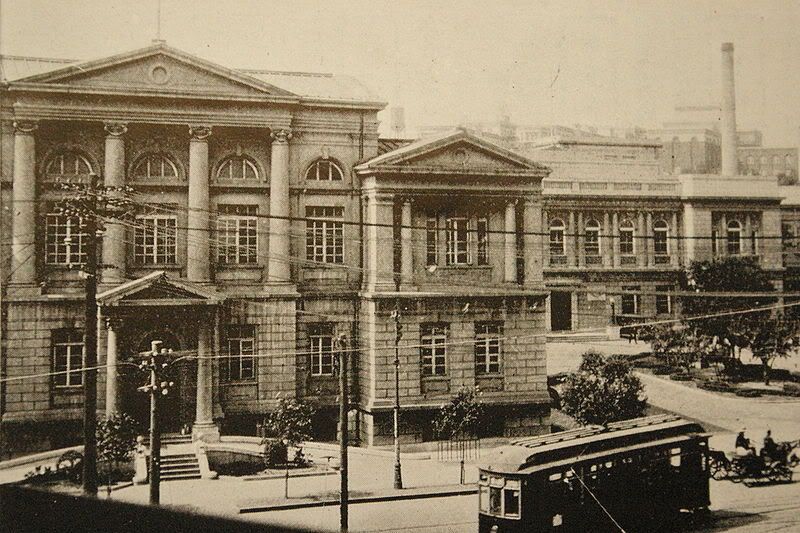 The headquarter of the South Manchurian Railroad in Dalian
The headquarter of the South Manchurian Railroad in Dalian