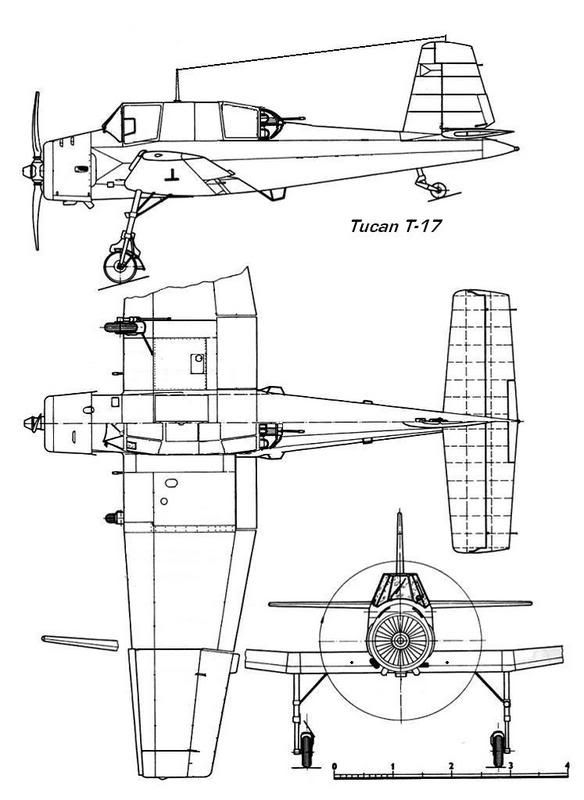
Developed as a carrier-based dive-bomber the NB-1 can also be used as a fighter in emergency situations or as a recconaisance type. Production has now ended.
Dimensions: span 14.05m; length 10.85; height 3.81m; wing area 28.98 sq m (46/ 35.7/ 12.6/ 312 sq ft)
Structure: all-metal monocoque fuselage in three sections with Z section fames and L section stringers with riveted stressed light alloy covering, light alloy used for cantilever tail construction and tailplane covering. Cantilever metal wing with two steel spars, all-metal split flaps and aluminium framed ailerons with fabric covering. Underwing hydraulic-operated aluminium dive-brakes. Rudder and elevators aluminium framed with fabric covering. Retractable main undercarriage with single oleo-pneumatic legs with pneumatic brakes, an un-retractable castoring tail wheel and catapult spools and retractable arrestor hook attached to the lower fuselage aft.
Weights: empty 5,712lbs, maximum take-off 8,000lbs
Powerplant: one 1000hp Spartan 1000 twin-row radial engine
Performance: max speed 270 mph; service ceiling 30,500ft; range 921 miles (800nm)
Capacity: pilot in enclosed cockpit forward, navigator/gunner behind in fuselage in enclosed cockpit facing aft, pilot protected by a 6mm thick armoured plate
Armament: four wing-mounted 7.62mm Browning MG, one manual dorsal mounting with 7.92mm FMG/M32 MG (drum feed), bombload 227kg (500lbs) on one ventral (500lbs) and two wing racks (250lbs each)
Equipment: full controls and navigation equipment including receiver/transmitter, Sperry autopilot, one rescue dinghy in wingroot and ventral camera fitted in cabin floor
Tucan T-18B NB-2
Designed as a one-off prototype, this was the prototype T-18 fitted with a Spartan inline engine and new nose section ahead of the cockpit. The fuselage was strengthened, a section inserted aft to maintain the cg, new undercarriage fitted, altered fuel system and some aerodynamic refinements added. It first flew on July 6 1938 and then went for trials with the Aviacion Naval. Since then it has been brought by both Chile and Brazil as a land-based attack aircraft and the FAA has ordered a batch of 40 as the NB-2 to replace the older NB-1 between 1940-41.
Dimensions: span 14.05m; length 11.7; height 3.81m; wing area 28.98 sq m (46/ 38.4/ 12.6/ 312 sq ft); wing loading 29 lbs/ft; power loading 0.16lb/hp
Structure: all-metal monocoque fuselage in three sections with Z section fames and L section stringers with riveted stressed light alloy covering, light alloy used for cantilever tail construction and tailplane covering. Cantilever metal wing with two steel spars of I section, all-metal split flaps and aluminium framed ailerons with aluminium covering. Rudder and elevators aluminium framed with aluminium covering. Underwing hydraulic-operated aluminium dive-brakes. Retractable main undercarriage with single oleo-pneumatic legs with pneumatic brakes and a retractable castoring tail wheel and catapult spools and retractable arrestor hook attached to the lower fuselage aft.
Weights: empty 6,969lbs, maximum take-off 9,000lbs
Powerplant: one 1300hp FMA Spartan 12V-1300S-SA V-12 inline engine with supercharger
Performance: max speed 324 mph; service ceiling 34,500ft; range 748 miles full load
Capacity: pilot in enclosed cockpit forward, navigator/gunner behind in fuselage in enclosed cockpit facing aft, pilot protected by a 6mm thick armoured plate
Armament: four wing-mounted 7.62mm Browning MG, one manual dorsal mounting with twin 7.92mm FMG/M32 MG (drum feed), bombload 227kg (500lbs) on one ventral (500lbs) and two wing racks (250lbs each)
Equipment: full controls and navigation equipment including receiver/transmitter, HF/DF, Sperry autopilot, one rescue dinghy in wingroot and ventral camera fitted in cabin floor